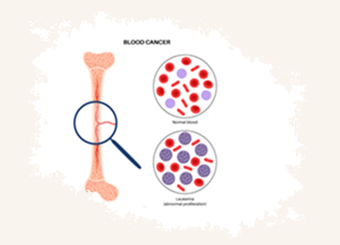
Multiple Myeloma: A Cancer of Plasma Cells
Multiple myeloma is a type of blood cancer that affects plasma cells, a type of white blood cell found in the bone marrow. These cells normally help the body fight infections by producing antibodies. However, in multiple myeloma, abnormal plasma cells multiply uncontrollably, crowding out healthy blood cells and producing abnormal proteins that can damage organs.
Symptoms of Multiple Myeloma:
Bone pain (especially in the back, ribs, or hips)
Fatigue and weakness due to anemia
Frequent infections due to weakened immunity
Kidney problems from abnormal protein buildup
High calcium levels leading to excessive thirst, nausea, and confusion
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Multiple myeloma is diagnosed through blood tests, urine tests, bone marrow biopsy, and imaging scans (X-ray, MRI, or PET scans).
While multiple myeloma is not curable, treatment can help manage the disease. Therapies include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, corticosteroids, and stem cell transplants. Supportive treatments like bone-strengthening medications and pain management also improve quality of life.
With advances in treatment, many patients achieve long-term remission, making early detection and personalized therapy essential for better outcomes.